About Linear Bearings
More
Linear Bearings for Ball Splines
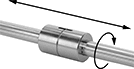
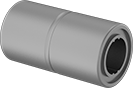
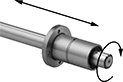
Combine these bearings with a ball spline to create a compact linear and rotary motion system for applications with fast, complex movements, such as robotics. These bearings move smoothly and precisely even at high speeds along ball splines while grooves on the ball spline transmit rotary power. Clip a retaining ring into the groove on these bearings to position them in your system. Use the keyway and included machine key for attaching your load.
Splines are alloy steel for high strength and wear resistance. They're hardened only on the outside, so they stand up to repeated motion while keeping their center soft enough to absorb stress from shifting loads. Those with a step-down end have a shoulder near the end to stop gears, sprockets, and bearings.

Groove | Keyway | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For Spline Dia., mm | For No. of Splines | Overall Lg., mm | OD, mm | Dynamic Load Capacity, lbs. | Static Load Capacity, lbs. | Max. Dynamic Torque, in.-lbs. | Max. Static Torque, in.-lbs. | Max. Temp., °F | With Retaining Ring Grooves | Wd., mm | Dia., mm | Includes | Lg., mm | Wd., mm | Dp., mm | Each | |
| 18.2 | 4 | 60 | 32 | 1,750 | 2,500 | 734 | 1,177 | 176° | Yes | 3.1 | 30.2 | Machine Key | 26 | 4 | 2.5 | 00000000 | 0000000 |


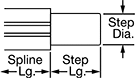
Step | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dia., mm | No. of Splines | Lg., mm | Spline Lg., mm | Root Dia., mm | Dia., mm | Lg., mm | Material | Each | |
Splined End × Step-Down End | |||||||||
| 18.2 | 4 | 350 | 200 | 16.4 | 15 | 150 | 52100 Alloy Steel | 00000000 | 0000000 |
Mounted Linear Bearings for Ball Splines
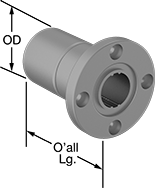
A flange with mounting holes makes it easy to attach a load to these bearings. Create a compact linear and rotary motion system for robots and other applications requiring complex, fast movements, by combining them with ball splines. These bearings move smoothly and precisely even at high speeds along ball splines while grooves on the ball spline transmit rotary power. Clip a retaining ring (not included) into the groove on these bearings to position them in your system.
Splines are alloy steel for high strength and wear resistance. They're hardened only on the outside, so they stand up to repeated motion while keeping their center soft enough to absorb stress from shifting loads. Those with a step-down end have a shoulder near the end to stop gears, sprockets, and bearings.

Groove | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
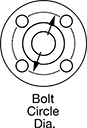
| For Spline Dia., mm | For No. of Splines | Overall Lg., mm | Flange OD, mm | Bolt Circle Dia., mm | OD, mm | Dynamic Load Capacity, lbs. | Static Load Capacity, lbs. | Max. Dynamic Torque, in.-lbs. | Max. Static Torque, in.-lbs. | Max. Temperature, ° F | With Retaining Ring Grooves | Wd., mm | Dia., mm | Number of Mounting Holes | Each | |
| 18.2 | 4 | 60 | 51 | 40 | 32 | 1,750 | 2,500 | 734 | 1,177 | 176° | Yes | 3 | 31.3 | 4 | 00000000 | 0000000 |




Step | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dia., mm | No. of Splines | Lg., mm | Spline Lg., mm | Root Dia., mm | Dia., mm | Lg., mm | Material | Each | |
Splined End × Step-Down End | |||||||||
| 18.2 | 4 | 350 | 200 | 16.4 | 15 | 150 | 52100 Alloy Steel | 00000000 | 0000000 |

























