Filter by
System of Measurement
OD
Rod End Type
Lubrication
Maximum Temperature
Insert Material
Material
Bearing Seal Type
Static Radial Load Capacity
Ball Finish
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
REACH
RoHS
Minimum Temperature
Ball Material
Relubrication
Liner Material
About Rod Ends
More
Swivel Joints
Open
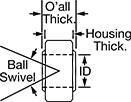
Also known as spherical bearings, swivel joints support angular misalignment. Press them into a hole or housing where a ball joint rod end won’t fit. They need to be lubricated when first installed and periodically after that. Apply any type of bearing grease to the ball, and rotate it to work it into the races.
| ID | OD | O'all Thick. | Housing Thick. | Max. Ball Swivel | Static Radial Load Cap., lbs. | Material | Each | |
Open | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mm | 56mm | 31mm | 22mm | 30° | 87,650 | Alloy Steel | 0000000 | 000000 |
Lubrication-Free Swivel Joints


A slippery PTFE liner reduces friction without the oily mess. Also known as spherical bearings, they support angular misalignment. Press them into a hole or housing where a ball joint rod end won’t fit.
| ID | OD | O'all Thick. | Housing Thick. | Max. Ball Swivel | Static Radial Load Cap., lbs. | Temp. Range, °F | Material | Each | |
| 25mm | 56mm | 31mm | 22mm | 30° | 87,650 | -65° to 275° | Alloy Steel | 0000000 | 000000 |

























