Filter by
System of Measurement
Material
Shaft Mount Type
Overall Length
Joint Type
Maximum Torque
Drive Style
Torque @ Motor Speed
Parallel Misalignment Capability
Length
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
Adjustable-Length Precision Double U-Joints
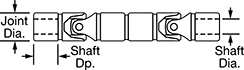
For Shaft | Torque | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dia. | Dp. | Joint Dia. | Overall Lg. | Max. Operating Angle | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Torque, in·lbf | 5° Operating Angle | 10° Operating Angle | Parallel Misalignment Capability | Joint Type | Adjustment Movement | For Shaft Type | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
303 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/4" | 3/8" | 3/8" | 2 3/4" to 3" | 30° | 4,000 | 16 | 14.4 in·lbf @ 1,500 rpm | 12.8 in·lbf @ 1,500 rpm | 0.7" | Ball Bearing | Telescope | Round | 60075K97 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
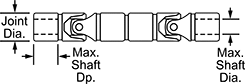
Double U-Joints
For Shaft | Torque | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dia. | Dp. | Joint Dia. | Overall Lg. | Max. Operating Angle | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Torque, in·lbf | 3° Operating Angle | 10° Operating Angle | Parallel Misalignment Capability | Joint Type | For Shaft Type | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/4" | 5/8" | 1/2" | 4" | 25° | 1,750 | 375 | 150 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 51 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 0.845" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K26 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5/16" | 11/16" | 5/8" | 4 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 540 | 245 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 83 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 0.951" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K56 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/8" | 7/8" | 3/4" | 5 3/8" | 25° | 1,750 | 765 | 330 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 110 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.133" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K83 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/2" | 1" | 1" | 6 3/4" | 25° | 1,750 | 1,560 | 595 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 200 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.428" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K57 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5/8" | 1 1/16" | 1 1/4" | 7 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 5,220 | 980 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 330 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.585" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K85 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/4" | 1 3/16" | 1 1/2" | 8 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 7,920 | 1,425 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 480 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.796" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K94 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
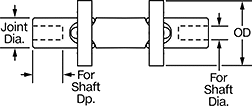
Precision Double U-Joints
For Shaft | Torque | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dia. | Dp. | Joint Dia. | Overall Lg. | OD | Max. Operating Angle | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Torque, in·lbf | 5° Operating Angle | 10° Operating Angle | Parallel Misalignment Capability | Joint Type | For Shaft Type | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
303 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/4" | 1/2" | 3/8" | 2 1/2" | — | 30° | 4,000 | 16 | 14.4 in·lbf @ 1,500 rpm | 12.8 in·lbf @ 1,500 rpm | 0.45" | Ball Bearing | Round | 60075K87 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/8" | 3/8" | 3/4" | 2 7/8" | 1 3/8" | 20° | 2,000 | 30 | 24.9 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 19.9 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 0.4" | Ball Bearing | Round | 3945N11 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/2" | 7/8" | 1" | 3 7/8" | 1 7/8" | 20° | 2,000 | 75 | 62.5 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 49.9 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 0.5" | Ball Bearing | Round | 3945N12 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5/8" | 7/8" | 1" | 3 7/8" | 1 7/8" | 20° | 2,000 | 75 | 62.5 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 49.9 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 0.5" | Ball Bearing | Round | 3945N13 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/4" | 7/8" | 1" | 3 7/8" | 1 7/8" | 20° | 2,000 | 75 | 62.5 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 49.9 in·lbf @ 1,000 rpm | 0.5" | Ball Bearing | Round | 3945N14 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1" | 1 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 6 3/4" | 2 1/2" | 10° | 1,500 | 600 | 468.7 in·lbf @ 750 rpm | 374.9 in·lbf @ 750 rpm | 0.75" | Ball Bearing | Round | 3945N15 | 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
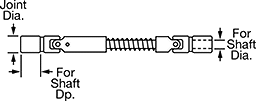
Quick-Change Adjustable-Length Double U-Joints
For Shaft | Keyway | Torque | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dia. | Dp. | Joint Dia. | Overall Lg. | Wd. | Dp. | Max. Operating Angle | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Torque, in·lbf | 3° Operating Angle | 10° Operating Angle | Parallel Misalignment Capability | Joint Type | For Shaft Type | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/8" | 15/16" | 3/4" | 11 1/4" to 14 1/4" | 3/32" | 3/64" | 35° | 1,000 | 600 | 335 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 100 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 6.63" | Pin and Block | Keyed | 4125N11 | 000000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/2" | 1 3/16" | 1" | 11 1/4" to 14 1/4" | 1/8" | 1/16" | 35° | 1,000 | 1,450 | 600 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 180 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 6.24" | Pin and Block | Keyed | 4125N12 | 00000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5/8" | 1 1/4" | 1 1/4" | 13 1/2" to 16 1/2" | 3/16" | 5/64" | 35° | 1,000 | 2,800 | 940 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 280 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 7.31" | Pin and Block | Keyed | 4125N13 | 00000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/4" | 1 3/8" | 1 1/2" | 14 3/4" to 17 3/4" | 3/16" | 3/32" | 35° | 1,000 | 4,350 | 1,450 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 435 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 7.74" | Pin and Block | Keyed | 4125N14 | 00000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1" | 1 11/16" | 2" | 17 1/2" to 20 1/2" | 1/4" | 7/64" | 35° | 1,000 | 7,350 | 2,450 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 735 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 8.6" | Pin and Block | Keyed | 4125N15 | 00000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Machinable-Bore Double U-Joints
Torque | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
For Max. Shaft Dia. | For Max. Shaft Dp. | Joint Dia. | Overall Lg. | Max. Operating Angle | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Torque, in·lbf | 3° Operating Angle | 10° Operating Angle | Parallel Misalignment Capability | Joint Type | For Shaft Type | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/8" | 5/8" | 1/2" | 4" | 25° | 1,750 | 375 | 150 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 51 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 0.845" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K15 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/2" | 11/16" | 5/8" | 4 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 540 | 245 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 83 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 0.951" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K52 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5/8" | 7/8" | 3/4" | 5 3/8" | 25° | 1,750 | 765 | 330 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 110 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.133" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K63 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3/4" | 1" | 1" | 6 3/4" | 25° | 1,750 | 1,560 | 595 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 200 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.428" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K55 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1" | 1 1/16" | 1 1/4" | 7 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 5,220 | 980 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 330 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.585" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K29 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 1/8" | 1 3/16" | 1 1/2" | 8 1/2" | 25° | 1,750 | 7,920 | 1,425 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 480 in·lbf @ 300 rpm | 1.796" | Pin and Block | Round | 6443K38 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||