Filter by
Thread Size
System of Measurement
Hex Nut Profile
Thread Spacing
Specifications Met
Material
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
REACH
RoHS
Drive Style
Thread Type
Fastener Strength Grade/Class
Fastener Strength Rating
Thread Fit
Thread Direction
Spanner Wrench Style
Thin-Profile Hex Nuts
 |
About half the height of standard-profile nuts, these fit in spaces with low clearance. You can also use them as jam nuts by threading them against another hex nut to hold it in place.
Medium-Strength Steel
These Grade 5 or Class 04 nuts are your go-to for fastening most machinery and equipment. To avoid stripped threads during installation, make sure your screw has a comparable strength rating.
Steel—Best for dry environments since moisture will cause these nuts to rust.
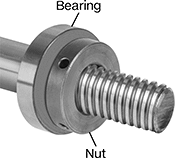
Thin-Profile Bearing Nuts
 |
 |
Used in pairs or with another bearing nut, these thin-profile nuts—often called shaft nuts—hold bearings, bushings, pulleys, and gears in place on your threaded shaft or spindle. Threading two nuts tightly against each other makes it harder for vibration to loosen your assembly than if you used only one nut. For the nut closer to the bearing, position the stepped face towards the bearing. These thin-profile nuts have holes on the side, so you can tighten and loosen them with a pin spanner wrench. All meet DIN 1816, an international standard for bearing locknut dimensions.
Carbon Steel—Carbon steel bearing nuts are strong and resist wear.
Thread Spacing—When choosing your thread spacing, consider the precision of your application. The finer the threads, the more control you have when making adjustments.
Thread | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Size | Spacing | OD, mm | Wd., mm | Specs. Met | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carbon Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepped Face | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M52 × 1.5 mm | Extra Fine | 80 | 13 | DIN 1816 | 3549N29 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

























