How to Identify and Measure Fittings
Pipe size is an industry designation, not the actual size. View information about how to measure threaded and unthreaded pipe and pipe fittings.
More
Nuts for High-Pressure Nipples for Compressed Gas
Slide a high-pressure hose nipple for compressed gas into one of these nuts to connect a pipe to the inlet of a pressure regulator. They are also known as CGA (Compressed Gas Association) nuts and inlet nuts.
316 stainless steel nuts have excellent corrosion resistance.
Nuts with left-hand threads are identified with a notch.
Note: Nuts have a CGA, BS, or DIN number that corresponds to a specific type of gas. Choose a nut with the same number as your tank and other system components.
- Maximum Pressure: See table
- Maximum Temperature: 120° F, except DIN 477 No. 9: 250° F
| Number | Thread Size | Thread Type | Thread Direction | Max. Pressure | For Use With | Each | |
316 Stainless Steel | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA 670 | 1.035"-14 | NGO | Left Hand | 3,000 psi @ 72° F | Hydrogen Fluoride, Nitrogen Trifluoride, Tungsten Hexafluoride | 000000000 | 000000 |
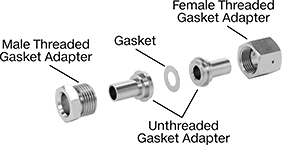
Ultra-High-Polish Gasket Fittings for Stainless Steel Tubing
- For Use With: Ammonia, Argon, Butane, Carbon Dioxide, Chloride, Fluoride, Fluorocarbon, Germane, Halide, Helium, Hydrogen, Krypton, Laser Gas, Natural Gas, Neon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Silane, Sulfur Hexafluoride, Tungsten Hexafluoride, Xenon
- Temperature Range: -420° to 1000° F
- Tubing: Use with 316/316L stainless steel
- Compatible With: Swagelok® VCR
Polished to at least a 15 Ra finish on the inside, these fittings have an ultra-smooth interior surface that helps prevent contamination. Also known as ultra-high-purity fittings, they’re packed in a Class 100 clean room, cleaned, and double bagged. They are commonly used in semiconductor applications. Fittings use a metal gasket (sold separately), which generates fewer particles than a rubber gasket and creates a strong seal in high-pressure and ultra-high-vacuum applications. Fittings are 316 stainless steel for excellent corrosion resistance.
To assemble, place a gasket between the gasket ends before gently rotating the female-threaded fitting onto the male-threaded fitting. Tighten until 1/8 of a turn past finger tight.
Choose threaded fittings to attach directly to other fittings.

| For Tube OD | Pipe Size | Material | Max. Pressure | Max. Vacuum | Interior Smoothness, Ra | Environmental Rating | Each | |
NPT Threads | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2" | 1/2 | 316L Stainless Steel | 3,500 psi @ 72° F | 10 -11 torr @ 72° F | 5 | Fed. Std. Class 100 | 0000000 | 000000 |

Retaining
Tabs
Nickel gaskets are softer than stainless steel gaskets, so they won’t wear down sealing surfaces as much, and they’re easier to tighten. They’re reactive to carbon monoxide and ozone, so they shouldn’t be used with those chemicals.
Hard and heat resistant, stainless steel gaskets can be used in a wider range of applications than nickel gaskets such as carbon monoxide and ozone. However, they’re harder to tighten than nickel gaskets, and they’ll wear down sealing surfaces more quickly.
Silver-plated stainless steel gaskets are softer than unfinished stainless steel gaskets, so they won’t wear down sealing surfaces as much, and they’re easier to tighten. However, they oxidize when exposed to air, and silver particles might flake off during assembly.
Gaskets with retaining tabs stay in place during installation, so you don’t have to hold the gasket while fastening fittings together. This also means they’re less likely to scratch or nick your fittings by rotating during installation.
| For Tube OD | Max. Vacuum | Environmental Rating | Each | |
Nickel Gasket | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2" | 10 -11 torr @ 72° F | Fed. Std. Class 100 | 00000000 | 00000 |
316L Stainless Steel Gasket | ||||
| 1/2" | 10 -11 torr @ 72° F | Fed. Std. Class 100 | 0000000 | 0000 |
Silver-Plated 316L Stainless Steel Gasket | ||||
| 1/2" | 10 -11 torr @ 72° F | Fed. Std. Class 100 | 00000000 | 0000 |
316L Stainless Steel Gasket with Retaining Tabs | ||||
| 1/2" | 10 -11 torr @ 72° F | Fed. Std. Class 100 | 00000000 | 0000 |