Filter by
Thread Size
Fitting Type
Gender
Fitting Connection
Material
Shape
System of Measurement
Connects To
For Use With
Thread Type
Maximum Pressure @ Temperature
Length
Maximum Temperature
Thread Direction
CGA Number
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
REACH
RoHS
Minimum Temperature
Tighten With
How to Identify and Measure Fittings
Pipe size is an industry designation, not the actual size. View information about how to measure threaded and unthreaded pipe and pipe fittings.
More
Nuts for High-Pressure Nipples for Compressed Gas
Slide a high-pressure hose nipple for compressed gas into one of these nuts to connect a pipe to the inlet of a pressure regulator. They are also known as CGA (Compressed Gas Association) nuts and inlet nuts.
Brass nuts have good corrosion resistance and are softer than 316 stainless steel nuts, so they're easier to thread together.
Note: Nuts have a CGA, BS, or DIN number that corresponds to a specific type of gas. Choose a nut with the same number as your tank and other system components.
Female
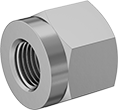
Female Nut
- Maximum Pressure: See table
- Maximum Temperature: 120° F, except DIN 477 No. 9: 250° F
| Number | Thread Size | Thread Type | Thread Direction | Max. Pressure | For Use With | Each | |
Brass | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA 280 | 0.750"-14 | NGO | Right Hand | 3,000 psi @ 72° F | Medical Gas Mixtures | 000000000 | 000000 |

























