Filter by
System of Measurement
Thread Size
Drive Style
Thread Spacing
Fastener Strength Grade/Class
Material
Hex Nut Profile
Thread Type
Fastener Strength Rating
Face Style
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
REACH
RoHS
Spanner Wrench Style
Thread Direction
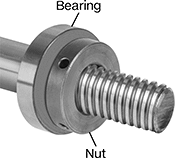
About Hex Nuts
Choose a hex nut with the right profile, material, and strength for your application.