Filter by
System of Measurement
Thread Size
Mount Type
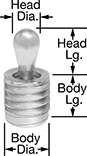
Head Diameter
Material
Body Material
Head Material
Body Diameter
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
REACH
Finish
Body Length
Head Length
Maximum Head Movement
Minimum Spring Force
Thread Type
Hardness
Pitch
Threaded Spring Locating Pins
Pins | Installation Tools | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Body, mm | Head, mm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thread Size | Dia. | Lg. | Dia. | Lg. | Max. Head Movement, mm | Min. Spring Force | Max. Spring Force, lbf | Body Dia. Tolerance, mm | Body Material | Each | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zinc-Plated Steel Head | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M18 × 1.5 mm | 16 | 18 | 10 | 16 | 1.6 | Not Rated | 33 | -0.15 to 0.15 | Steel | 0000000 | 00000 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M18 × 1.5 mm | 16 | 18 | 10 | 16 | 1.6 | Not Rated | 45 | -0.15 to 0.15 | Steel | 0000000 | 0000 | 0000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Threaded Hole Location Gauges
Thread Size | Thread Type | Hardness | Material | Each | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M18 × 1.5 mm | Metric | Rockwell C60 | Tool Steel | 0000000 | 0000000 |