Filter by
Starting Torque
Speed @ Continuous Operating Torque
Continuous Operating Torque
Voltage
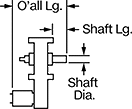
Shaft Diameter
Bearing Type
Motor Enclosure Type
Mounting Position
Gear Material
Motor Type
Face Shape
Gear Type
Shaft Length
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
Insulation Class
Insulation Maximum Temperature
Maximum Rotation Speed
REACH
RoHS
Service Factor
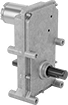
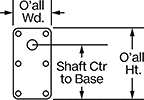
Shaft Center-to-Base Length
Duty Cycle
Enclosure Material
Radial Load Capacity
About Electric Motors
When replacing a motor, use the information on your motor’s nameplate to guide your selection.
More
Compact DC Gearmotors
Drive low-speed, high-torque applications in small spaces. Gearmotors combine a motor and speed reducer to lower speed and increase torque. Wire for clockwise or counterclockwise rotation.
Use a motor speed control (not included) to adjust the motor speed. To convert AC power to DC power, see AC to DC transformers.
Use a torque-speed curve to confirm which motor will work for your application. Click on a part number and select “Product Detail” to view the curve for a motor.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
Rectangular Face
Overall | Shaft | Insulation | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed @ Continuous Operating Torque | Power, hp | Full Load Current, A | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Bearing Type | Dia. | Lg. | Center to Base | Class | Max. Temp., °F | Each | |
12 Volts DC | |||||||||||||
| 0.5 rpm @ 2,400 in.-oz. | 0.002 | 0.3 | 3 3/4" | 2 3/4" | 4 5/8" | Plain | 1/2" | 7/8" | 1.38" | B | 266° | 00000000 | 0000000 |

























