Filter by
Maximum Rotation Speed
Speed @ Continuous Operating Torque
Voltage
Continuous Operating Torque
Starting Torque
Face Shape
Voltage Type
Motor Type
Shaft Diameter
Shaft Orientation
Bearing Type
Shaft Type
Mounting Position
DFARS Specialty Metals
Duty Cycle
Efficiency
Electrical Connection
Enclosure Finish
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
Gear Type
REACH
RoHS
U.S.–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) Qualifying
Height
Compact DC Gearmotors
Round Face
 | 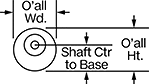 | 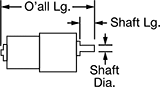 |
Overall | Shaft | Insulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Speed @ Continuous Operating Torque | Power, hp | Full Load Current, amp | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Bearing Type | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Class | Max. Temp., ° F | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
19.1V DC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 65 rpm @ 46 in·ozf | 0.0032 | 0.6 | 3 3/4" | 1 3/8" | 1 3/8" | Plain | 0.19" | 3/4" | 0.95" | F | 311 | 2709K13 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EachIn stock Select a compatible file type: Parasolid Solidworks 2022 and Parasolid files now available Solidworks 2022, PDF, and DWG files now available Parasolid files now available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||