Miniature Carbide Square End Mills
With a mill diameter less than 1/8" or 3 mm, these end mills are great for precise, detailed work such as in electronics, mold making, and medical-device manufacturing. They have a square end for milling square-bottomed slots, pockets, and edges. All are center cutting, allowing plunge cuts into a surface.
Made of solid carbide, these end mills are harder, stronger, and more wear resistant than high-speed steel and cobalt steel for the longest life and best finish. Their extreme hardness means they are brittle, so a highly rigid setup, such as a CNC machine, is necessary to prevent the end mill from breaking.
End mills with fewer flutes provide better chip clearance for high-volume, high-speed plunge, slotting, and roughing cuts; end mills with more flutes provide a finer finish and operate with less vibration when run at high speeds.
Use uncoated end mills for general purpose milling and short production runs. They stay sharper than coated end mills when used on soft materials like aluminum, leaving a better finish.
| Mill Dia. | Shank Dia. | Lg. of Cut | O'all Lg. | Flute Spacing | Helix Angle | For Use On | End Mill Type | Each | |
Uncoated | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2 Flute | |||||||||
| 0.7mm | 3mm | 2.1mm | 38mm | Equal | 30° | Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Iron, Nickel, Plastic, Stainless Steel, Steel, Titanium, Tool Steel | Center Cutting | 0000000 | 000000 |
Long-Reach Carbide Ball End Mills for Mold Making
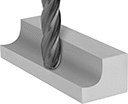
These end mills have an extended neck with a reduced diameter that prevents them from rubbing against your workpiece when deep milling. Also known as runner cutters, they cut channels with precise angles and dimensions, reducing the need for additional finishing. They have a ball end for milling rounded slots, slopes, and contours. All are center cutting, allowing plunge cuts into a surface.
Made of solid carbide, these end mills are harder, stronger, and more wear resistant than high-speed steel and cobalt steel for the longest life and best finish on hard material. Their extreme hardness means they are brittle, so a highly rigid setup, such as a CNC machine, is necessary to prevent the end mill from breaking.
Use uncoated end mills for general purpose milling and short production runs. They will stay sharper than coated end mills and leave a better finish on soft materials like aluminum.
End mills with fewer flutes provide better chip clearance for high-volume, high-speed plunge, slotting, and roughing cuts; end mills with more flutes provide a finer finish and operate with less vibration when run at high speeds.
Neck | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mill Dia. | Shank Dia. | Dia. | Lg. | Lg. of Cut | Overall Lg. | Flute Spacing | Helix Angle | For Use On | End Mill Type | Each | |
Uncoated | |||||||||||
2 Flute | |||||||||||
| 0.7mm | 4mm | 0.68mm | 4.3mm | 0.7mm | 50mm | Equal | 30° | Aluminum, Brass, Bronze, Copper, Fiberglass, Hardened Steel, Iron, Nickel, Plastic, Stainless Steel, Steel, Titanium, Tool Steel | Center Cutting | 0000000 | 0000000 |