Filter by
Finish
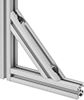
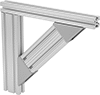
Shape
Base Thickness
Leg Thickness
DFARS Specialty Metals
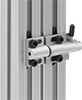
Frame Material
Raw Materials
Building and Machinery Hardware
Material Handling
Facility and Grounds Maintenance
Electrical
Fabricating and Machining
Fastening and Joining
Power Transmission
Containers, Storage, and Furniture
Lighting
Fluid Handling