Filter by
Diameter
System of Measurement
Material
End Type
Specifications Met
Tolerance Rating
Passivation
DFARS Specialty Metals
Steel Grade
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
Head Diameter
Hole Diameter
Finish
Head Height
Cotter Pin Type
Dowel Pins
Precisely align machine parts and prevent movement during assembly. These dowel pins are machined to tight tolerances and have a uniform diameter for a snug fit. They can also be used as a pivot, shaft, or hinge to join moving components. Since dowel pins can be hard to remove, they are best suited for permanent fixtures that don't require frequent adjustments or disassembly.
Steel
High-Strength Alloy Steel—Our strongest, most wear-resistant pins, these won't bend or break from vibration. Use them for high-stress applications, such as mounting and aligning hydraulic cylinders and injection molds. They perform best in dry environments since moisture will cause them to rust.
Lg., mm | Dia. Tolerance, mm | Double Shear Breaking Strength | Min. Hardness | Specs. Met | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
High-Strength Alloy Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C52 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A951 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C52 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A952 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C52 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A953 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C52 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A954 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C52 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A955 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C58 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 50 | 91595A129 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Rockwell C58 | DIN 6325-m6, ISO 8734 | 25 | 91595A172 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel
18-8 Stainless Steel—The choice for wet and outdoor environments. In addition to resisting rust, these pins also withstand mild chemicals such as cleaners and degreasers. They are strong enough to join most components but won't withstand extreme stress and vibration as well as steel.
Super-Corrosion-Resistant 316 Stainless Steel—Our most corrosion-resistant pins, these hold up in just about any environment. They won't degrade from exposure to weather, salt water, and most chemicals. Like 18-8 stainless steel, they're strong enough to join most components but won't withstand stress and vibration as well as steel.
Lg., mm | Dia. Tolerance, mm | Double Shear Breaking Strength | Min. Hardness | Specs. Met | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
18-8 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A032 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A034 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A035 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A058 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 91585A324 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A062 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 91585A325 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A091 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 50 | 91585A224 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 100 | 91585A909 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 0 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 50 | 91585A260 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 0 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 50 | 91585A268 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 50 | 91585A093 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 91585A326 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 91585A327 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Super-Corrosion-Resistant 316 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A030 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A031 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A032 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A121 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A033 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A124 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A034 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 0 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 10 | 93600A113 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A126 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A127 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A128 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A131 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A132 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 0.002 to 0.008 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 2338-m6 | 5 | 93600A134 | 0000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Captive Pins
Also known as pilot pins, use these pins to position, pivot, and align components. To install, punch or drill a hole in sheet metal, then use a punch and anvil or arbor press to clinch the head to the metal.
Pins are passivated for added protection against corrosion and oxidation. The ends are chamfered for easy insertion.
MPP PEM® Series—MPP PEM® Series pins work with most materials. Made of A286 stainless steel, they're our strongest captive pins, with corrosion resistance comparable to 18-8 stainless steel pins. They are nonmagnetic.
Lg., mm | Dia. Tolerance, mm | PEM® Series No. | PEM® Part No. | For Min. Panel Thk., mm | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A286 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | -0.038 to 0.038 | MPP | MPP-1MM-2 | 0.5 | 25 | 95648A110 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | -0.038 to 0.038 | MPP | MPP-1MM-3 | 0.5 | 25 | 95648A120 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | -0.038 to 0.038 | MPP | MPP-1MM-4 | 0.5 | 25 | 95648A130 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | -0.038 to 0.038 | MPP | MPP-1MM-5 | 0.5 | 25 | 95648A140 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Core Pins
Mold plastic around these pins to form small holes, or use them to perforate parts. They have a flat head to fit into a counterbored hole. Pins can be machined to fit your application. They're precision-ground to tight tolerances.
M2 High-Speed Tool Steel
M2 high-speed tool steel pins resist wear and stay sharp at high temperatures.
Head, mm | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Dia., mm | Dia. Tolerance, mm | Dia. | Ht. | Min. Hardness | 1-9 | 10-99 | 100-Up | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
63 mm Long | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.000 | 0 to 0.008 | 3 | 5 | Rockwell C60 | 98378A144 | 000000 | 000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Slotted Spring Pins
 |
End View |
Squeeze these pins into holes and they expand slightly, creating tension to hold parts in place. They are often used as hinge pins and as fasteners for springs and power transmission components. An alternative to dowel pins, they're lighter in weight with a hollow center and don’t need a precise hole. Also known as roll pins.
Spring Steel—These pins won't deform from stress and vibration. Although they're stronger than stainless steel, they're best for dry environments since moisture will cause them to rust.
Corrosion-Resistant 18-8 Stainless Steel—The choice for wet and outdoor environments, these pins resist rusting. They are strong enough to join most components but won't withstand extreme stress and vibration as well as steel.
Lg., mm | For Hole Dia., mm | Wall Thk., mm | Double Shear Breaking Strength, lbf | Min. Hardness | Specs. Met | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Spring Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 150 | Rockwell C42 | DIN 1481, ISO 8752 | 100 | 91611A065 | 00000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 0.2 | 150 | Rockwell C42 | ISO 8752 | 100 | 91611A067 | 0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 1 | 0.2 | 150 | Rockwell C42 | ISO 8752 | 100 | 91611A069 | 0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corrosion-Resistant 18-8 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 0.2 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 8752 | 100 | 91610A080 | 0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 0.2 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 8752 | 100 | 91610A082 | 0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 1 | 0.2 | Not Rated | Not Rated | ISO 8752 | 100 | 91610A084 | 0000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cotter Pins
Lock the ends of clevis pins and shafts to keep components in place. Slide these cotter pins into a hole and then bend the prongs outward with pliers to secure. Also known as split pins, one prong is slightly longer than the other for easy opening once inserted. Repeated bending will weaken the pin, so they should not be reused.
Steel
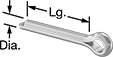 |
Zinc-Plated Spring Steel—These pins withstand occasional exposure to moisture. However, since friction from moving parts can wear away the finish, they're not ideal for wet environments. While not nearly as corrosion resistant as stainless steel, they are stronger and won’t deform under stress.
Undersized Dowel Pins
You don’t need to create precise holes for these pins when aligning parts you plan to bolt together. They have a slightly undersized diameter to slip into place without the need for special installation tools, like an arbor press. Undersized pins are also used for prototyping and positioning components you need to assemble and disassemble frequently.
Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel
 |
18-8 Stainless Steel—The choice for wet and outdoor environments. In addition to resisting rust, these pins also withstand mild chemicals such as cleaners and degreasers. They are strong enough to join most components but won't withstand extreme stress and vibration as well as steel.
Lg., mm | Dia. Tolerance, mm | Double Shear Breaking Strength | Min. Hardness | Specs. Met | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
18-8 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | -0.014 to 0 | Not Rated | Rockwell B95 | ISO 2338-h8 | 100 | 97049A301 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | -0.014 to 0 | Not Rated | Rockwell B95 | ISO 2338-h8 | 100 | 97049A302 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | -0.014 to 0 | Not Rated | Rockwell B95 | ISO 2338-h8 | 100 | 97049A303 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coiled Spring Pins
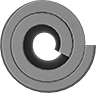 |
End View |
The best spring pins for joining parts exposed to vibration and shock. They're often used in power transmission, automation, and other assemblies with constant motion and sudden starts and stops. Because of their spiral shape, they flex to conform to holes that aren’t perfectly round.
Spring Steel—These pins won't deform from stress and vibration. Although they're stronger than stainless steel, they're best for dry environments since moisture will cause them to rust.
Corrosion-Resistant 18-8 Stainless Steel—The choice for wet and outdoor environments, these pins resist rusting. They are strong enough to join most components but won't withstand extreme stress and vibration as well as steel.
Lg., mm | For Hole Dia., mm | Double Shear Breaking Strength, lbf | Min. Hardness | Specs. Met | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Spring Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1.000 to 1.040 | 130 | Rockwell C43 | DIN 7343, ISO 8750 | 50 | 91612A205 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1.000 to 1.040 | 130 | Rockwell C43 | DIN 7343, ISO 8750 | 50 | 91612A207 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corrosion-Resistant 18-8 Stainless Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 mm Diameter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1.000 to 1.040 | 100 | Not Rated | DIN 7343, ISO 8750 | 50 | 91612A101 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1.000 to 1.040 | 100 | Not Rated | DIN 7343, ISO 8750 | 50 | 91612A103 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 1.000 to 1.040 | 100 | Not Rated | DIN 7343, ISO 8750 | 50 | 91612A107 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

























