How to Prime Your Pump
More
How to Determine Feet of Head
More
About Process Pumps
More
Constant-Flow-Rate Pumps without Motor for Chemicals
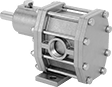
With a 316 stainless steel housing and stainless steel gears, these pumps are often used to dispense chemicals such as ethylene glycol, isopropyl alcohol, and nitric acid. Use an electric motor with a coupling and belt/pulley drive. Also known as gear pumps, they produce a smooth flow of liquid. All are self-priming, which means they create a suction force to draw liquid upward and fill the pump chamber. Do not use with solids.
Required hp | Intake (NPT) | Discharge (NPT) | Overall | Shaft | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. Flow Rate @ 25 psi, gpm | Max. Flow Rate, gpm | Max. ft. of Head | Max. Pressure, psi | Max. Viscosity, cP | @ 25 psi | @ 100 psi | Pipe Size | Gender | Pipe Size | Gender | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Center-to-Base Lg. | Each | |
| 4.3 | 4 | 346.3 | 150 | 20,000 | 1/4 | 3/4 | 1/2 | Female | 1/2 | Female | 6 1/4" | 3" | 3 3/4" | 1/2" | 1 1/4" | 2 5/8" | 00000000 | 000000000 |
| 10.2 | 10 | 346.3 | 150 | 20,000 | 1/2 | 1 1/2 hp | 3/4 | Female | 3/4 | Female | 7 1/2" | 3 3/8" | 4 3/8" | 5/8" | 1 3/4" | 3" | 00000000 | 00000000 |
High-Pressure Constant-Flow-Rate Pumps without Motor for Water

Commonly called rotary vane pumps, they have a built-in bypass relief valve to prevent pressure buildup. Attach an electric motor with a speed reducer or a belt pulley to alter the pump speed. Use a NEMA 56C frame motor. Pumps are gravity fed and require an elevated liquid source to fully fill the pump before turning on. Do not run dry or use with solids. They meet NSF/ANSI 61 safety standards for use with drinking water systems.
Pumps with a 303 stainless steel housing are more corrosion resistant than pumps with a brass housing.
Intake (NPT) | Discharge (NPT) | Overall | Shaft | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. Flow Rate, gpm | Max. ft. of Head | Max. Pressure, psi | Max. Viscosity | For Motor Power Source | Required hp | Pipe Size | Gender | Pipe Size | Gender | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Lg. | Wd. | Dp. | Center-to-Base Lg. | Each | |
303 Stainless Steel Housing | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2.3 | 554 | 240 | Not Rated | Electric | 1/2 | 3/8 | Female | 3/8 | Female | 7" | 7" | 6" | 7/16" | 1/4" | 3/8" | 3" | 00000000 | 0000000 |
| 4.3 | 554 | 240 | Not Rated | Electric | 3/4 | 1/2 | Female | 1/2 | Female | 7" | 7" | 6" | 7/16" | 1/4" | 3/8" | 3" | 00000000 | 000000 |
| 5.4 | 554 | 240 | Not Rated | Electric | 1 | 1/2 | Female | 1/2 | Female | 7" | 7" | 6" | 7/16" | 1/4" | 3/8" | 3" | 00000000 | 000000 |
Air-Powered Constant-Flow-Rate Pumps
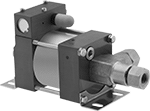
Commonly called piston pumps, these are often used in high-pressure applications, such as hydrostatic testing of pipelines, tanks, and valves. Flow and outlet liquid pressure can be controlled by varying the air pressure. To calculate discharge liquid pressure, multiply the air pressure by the ratio shown in the table. Pumps are self-priming, which means they create a suction force to draw liquid upward to fill the pump chamber.
Note: Pumps must be filled with liquid before use. They need a constant flow of liquid and cannot run dry.
Flow Rate, gpm | Air Pressure, psi | Overall | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @ 0 psi | @ 3,000 psi | Max. ft. of Head | Max. Discharge Pressure, psi | Max. Viscosity, cP | Min. | Max. | Air Consumption, scfm | Air Connection (NPT) | Intake Pipe Connection (NPT) | Discharge Pipe Connection (NPT) | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Each | |
86:1 Discharge Liquid to Inlet Air Pressure Ratio | |||||||||||||||
| 0.19 | 0.17 | 28,764 | 12,470 | 100 | 15 | 145 | 20 | 1/4 Female | 3/8 Female | 1/4 Female | 4 5/8" | 4" | 9" | 0000000 | 000000000 |
28:1 Discharge Liquid to Inlet Air Pressure Ratio | |||||||||||||||
| 0.58 | 0.13 | 9,365 | 4,060 | 100 | 15 | 145 | 20 | 1/4 Female | 3/8 Female | 1/4 Female | 4 5/8" | 4" | 9" | 0000000 | 00000000 |
11:1 Discharge Liquid to Inlet Air Pressure Ratio | |||||||||||||||
| 4.76 | __ | 3,679 | 1,595 | 100 | 15 | 145 | 45 | 1/2 Female | 1 Female | 1/2 Female | 10 3/4" | 7" | 12 1/4" | 0000000 | 00000000 |

























