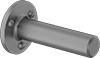
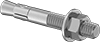
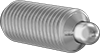
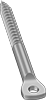Filter by
Material
Thread Direction
Thread Spacing
Shaft Length
Shoulder Diameter
Shoulder Length
Thread Pitch
Diameter
Fastener Strength Grade/Class
PEM® Part Number
DFARS Specialty Metals
Body Material
Bracket Material
Fastening and Joining
Fabricating and Machining
Power Transmission
Building and Machinery Hardware
Fluid Handling
Material Handling