Filter by
Motor Frame Size
Body Shape
System of Measurement
Shaft Diameter
Shaft Type
Overall Width
Number of Shafts
Maximum Holding Torque
Lead Screw Type
Thrust Load Capacity
Shaft Length
Mounting Position
Wire Connection
Component
Direction of Operation
Threading
U.S.–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) Qualifying
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
DFARS Specialty Metals
Stepper Motors
Motors
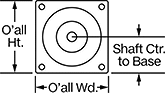
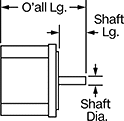
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia., mm | Lg., mm | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | No. of Shafts | Min. | Max. | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 8 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.2 | 2,450 | 0.5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 1.9" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4 | 8.5 | 0.4" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 6627T121 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 3,250 | 0.9 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.3" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4 | 8.5 | 0.4" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 6627T131 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepper Motors with Linear Actuation
Overall | Temp. Range, ° F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Travel Distance per Full Step | Travel Lg. | Dynamic Load Cap., lb. | Max. Speed, in/sec | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Lead Screw Lg. | Thread Size | Min. | Max. | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External Lead Screw | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
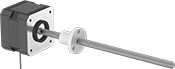 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 8 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00006" | 3.3" | 10 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | 9/64"-83.3 | 35 | 130 | 8677N37 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00006" | 7.3" | 10 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 9.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | 9/64"-83.3 | 35 | 130 | 8677N38 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00019" | 3.3" | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N39 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00019" | 7.3" | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 9.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N41 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 3.3" | 3 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N42 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 3.3" | 7 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.5" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N43 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 7.3" | 3 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 9.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N44 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 7.3" | 7 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 9.5" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N45 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pass-Through Lead Screw | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
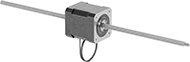 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 8 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00006" | 2.8" | 10 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | 9/64"-83.3 | 35 | 130 | 8677N66 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00006" | 6.8" | 10 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 8.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | 9/64"-83.3 | 35 | 130 | 8677N67 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00019" | 2.8" | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N68 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00019" | 6.8" | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 8.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N69 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 2.4" | 3 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N72 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 2.8" | 3 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N71 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 6.8" | 3 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 8.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N73 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.00078" | 6.8" | 3 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 8.1" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 8" | M3.5 × 1 mm | 35 | 130 | 8677N74 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||