Filter by
Maximum Holding Torque
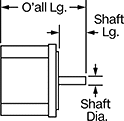
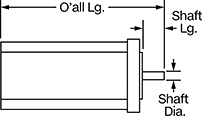
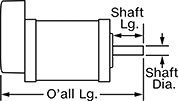
Overall Length
Shaft Length
Voltage
Component
Mounting Position
Direction of Operation
Thrust Load Capacity
Maximum Rotation Speed
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
RoHS
REACH
U.S.–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) Qualifying
DFARS Specialty Metals
Stepper Motors
Motors
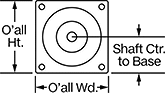
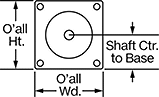
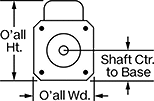
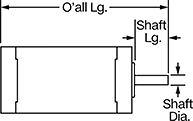
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | No. of Shafts | Min. | Max. | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 8 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.2 | 2,450 | 0.5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 1.9" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4 mm | 8.5 mm | 0.4" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 3,250 | 0.9 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.3" | 0.8" | 0.8" | 4 mm | 8.5 mm | 0.4" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 14 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 56.6 | 3,000 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.1" | 1.4" | 1.4" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | 1,300 | 0.67 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 1.9" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 4.5 mm | 20.3 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 62.3 | 1,200 | 0.84 | 0.9° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.8" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 71 | 2,475 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.5" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 4.5 mm | 20.3 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 84 | 820 | 1.05 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.6" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 24 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 115 | 1,000 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.8" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 125 | 975 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.1" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 24 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 73 | 1,800 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 2.6" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | 3,000 | 4.2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 2.4" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 173.5 | 1,000 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 173.9 | 1,000 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.6" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 178 | 2,700 | 5.6 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 198.2 | 400 | 1.5 | 0.9° | Bipolar | 4 | 3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 205 | 750 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3.9" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 237 | 1,175 | 4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.9" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 262 | 3,000 | 7 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3.8" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 339.8 | 250 | 1.5 | 0.9° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.9" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 425 | 2,100 | 7.06 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 5.3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 467.3 | 300 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.8" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 600.4 | 1,300 | 6.5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.2" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 24 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 153 | 2,100 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 2.7" | 2.4" | 2.4" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.18" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 229 | 2,100 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3" | 2.4" | 2.4" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.18" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 292 | 3,000 | 5.6 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3.5" | 2.4" | 2.4" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.18" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 380 | 2,400 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 3.8" | 2.4" | 2.4" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.18" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 431 | 1,800 | 5.6 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 4.3" | 2.4" | 2.4" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.18" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 34 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 362 | 750 | 6.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 4.1" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 3/8" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 470 | 4,000 | 4.2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 595 | 675 | 6.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 5.3" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 3/8" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 870 | 750 | 4.2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.3" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,140 | 300 | 6.3 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 8 | 6.5" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 3/8" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,435 | 250 | 4.83 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 6.5" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Round Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 14 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.5 | 825 | 0.6 | 0.9° | Bipolar | 4 | 1.6" | 1.4" | 1.4" | 5 mm | 18.2 mm | 0.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.5 | 1,475 | 1.2 | 0.9° | Bipolar | 4 | 1.6" | 1.4" | 1.4" | 5 mm | 18.2 mm | 0.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 00000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Motor/Drives
Current per Phase, amp | Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Min. | Max. | Voltage, V DC | Full Step Increment | Step Resolution | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | Min. | Max. | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | 660 | 0.07 | 0.71 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | Bipolar | 7 | 3.2" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 21.8 mm | 0.85" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | 720 | 0.08 | 0.85 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | Bipolar | 7 | 3.4" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 21.8 mm | 0.85" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 62 | 720 | 0.08 | 0.85 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | Bipolar | 7 | 3.7" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 21.8 mm | 0.85" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/8, 1/64, 1/256 | Bipolar | 7 | 3.8" | 2.2" | 2.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 175 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/8, 1/64, 1/256 | Bipolar | 7 | 4.2" | 2.2" | 2.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 262 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/8, 1/64, 1/256 | Bipolar | 7 | 5.1" | 2.2" | 2.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 425 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/8, 1/64, 1/256 | Bipolar | 7 | 6.6" | 2.2" | 2.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Motor/Encoders
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Voltage, V DC | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | Encoder Positioning Type | No. of Counts per Rev. | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | No. of Shafts | Min. | Max. | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26.9 | 1,500 | 0.67 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 2.6" | 2.3" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 70.8 | 3,000 | 2 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 3.2" | 2.3" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 83.5 | 825 | 1.05 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 3.5" | 2.3" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 124.6 | 1,400 | 2 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 3.9" | 2.3" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 181 | 600 | 2.8 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 3.7" | 2.6" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 237 | 525 | 4 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 4.6" | 2.6" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 355 | 900 | 6 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 4.9" | 2.6" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 467.3 | 300 | 2 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 4.5" | 2.5" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.11" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 600.4 | 1,300 | 6.5 | 5 | 1.8° | Bipolar | Incremental | 1,000 | 4 | 4.9" | 2.6" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 2 | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepper Gearmotors
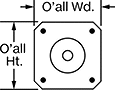
Overall | Shaft | Keyway, mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia., mm | Lg., mm | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | Lg. | Wd. | Dp. | Temp. Range, ° F | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 280 | 400 | 0.7 | 0.36° | 4 | 3.3" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 | 29 | 0.84" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 560 | 400 | 2 | 0.36° | 4 | 4" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 | 29 | 0.84" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,465 | 400 | 2.2 | 0.36° | 4 | 6.4" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2,102 | 400 | 5 | 0.36° | 4 | 7.2" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2,931 | 200 | 2.2 | 0.18° | 4 | 6.4" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4,205 | 200 | 5 | 0.18° | 4 | 7.2" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5,537 | 100 | 2.2 | 0.09° | 4 | 7.2" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7,944 | 100 | 5 | 0.09° | 4 | 8.1" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13,842 | 40 | 2.2 | 0.036° | 4 | 7.2" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19,681 | 40 | 5 | 0.036° | 4 | 8.1" | 2.6" | 2.6" | 16 | 29.5 | 1.18" | D-Profile | 25 | 5 | 3 | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Round Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 5 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.8 | 680 | 0.56 | 1.875° | 4 | 2.6" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.8 | 680 | 0.9 | 1.875° | 4 | 2.6" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41.7 | 40 | 0.56 | 0.11° | 4 | 2.9" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41.7 | 40 | 0.9 | 0.11° | 4 | 2.9" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41.7 | 165 | 0.56 | 0.45° | 4 | 2.8" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41.7 | 165 | 0.9 | 0.45° | 4 | 2.8" | 0.5" | 0.5" | 3 | 8.5 | 0.26" | D-Profile | — | — | — | 0 to 120 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepper Motors with Integrated Motion Control
 |
Current per Phase, amp | Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Min. | Max. | Voltage, V DC | Full Step Increment | Step Resolution | No. of Inputs/Outputs | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | Min. | Max. | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Motor/Controller/Drives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | 2 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 3.7" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.17" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 175 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | 2 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 4.3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.17" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 262 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | 2 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 5.1" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.17" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 425 | 1,500 | 0.21 | 2.1 | 12 to 24 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 | 2 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 6.6" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 13/16" | 1.17" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Motor/Controller/Drive/Encoders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3,000 | 0.1 | 2.2 | 12 to 48 | 1.8° | 1 to 1/256 | 1 Analog-Input, 3 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 3.7" | 1.7" | 3" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 35 | 100 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54 | 3,000 | 0.1 | 2.2 | 12 to 48 | 1.8° | 1 to 1/256 | 1 Analog-Input, 3 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 3.9" | 1.7" | 3" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 35 | 100 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 68 | 3,000 | 0.1 | 2.2 | 12 to 48 | 1.8° | 1 to 1/256 | 1 Analog-Input, 3 Digital-Inputs, 1 Digital-Output | 4.2" | 1.7" | 3" | 5 mm | 22 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 35 | 100 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 100.5 | 2,475 | 0.3 | 3 | 12 to 40 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/64, 1/128, 1/256 | 4 Digital-Inputs/Outputs | 3.8" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 182.5 | 2,000 | 0.3 | 3 | 12 to 40 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/64, 1/128, 1/256 | 4 Digital-Inputs/Outputs | 4.3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 294.5 | 820 | 0.3 | 3 | 12 to 40 | 1.8° | 1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/64, 1/128, 1/256 | 4 Digital-Inputs/Outputs | 5.1" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 0 | 120 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 24 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 340 | 2,400 | 3 | 5 | 12 to 70 | 1.8° | 1 to 1/256 | 1 Analog-Input, 4 Digital-Inputs/Outputs | 4.9" | 2.4" | 3.8" | 8 mm | 21 mm | 1.18" | D-Profile | 35 | 100 | 00000000 | 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wet-Environment Stepper Motors
Motors
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | No. of Shafts | Min. | Max. | Enclosure Rating | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 125 | 975 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.6" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 24 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 173.5 | 1,000 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.1" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 237 | 1,175 | 4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 274 | 820 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 352.5 | 3,000 | 6 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.4" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 34 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 470 | 4,000 | 4.2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4.1" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 910 | 410 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 5.4" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 3/8" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,435 | 250 | 4.83 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 6.4" | 3.4" | 3.4" | 1/2" | 1 1/2" | 1.7" | D-Profile | 1 | 0 | 120 | IP65 | 00000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stepper Servomotors with Integrated Drive
 |
Overall | Shaft | No. of Inputs/Outputs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Voltage, V DC | Current, amp | Step Resolution | Full Step Increment | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Communication Protocol | Digital Inputs | Analog Inputs | Digital Outputs | Enclosure Rating | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 11 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.2 | 3,000 | 15 to 30 | 0.9 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 2.7" | 1.1" | 1.5" | 5 mm | 13 mm | 0.57" | Modbus RTU | 4 | — | 2 | IP20 | 0000000 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11.3 | 3,000 | 15 to 30 | 1 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 3" | 1.1" | 1.5" | 5 mm | 13 mm | 0.57" | Modbus RTU | 4 | — | 2 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17.7 | 3,000 | 15 to 30 | 1 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 3.5" | 1.1" | 1.5" | 5 mm | 13 mm | 0.57" | Modbus RTU | 4 | — | 2 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | 3,000 | 12 to 48 | 1.3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 3.5" | 1.7" | 3" | 6 mm | 18 mm | 0.83" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | 3,000 | 12 to 48 | 1.4 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 3.7" | 1.7" | 3" | 6 mm | 18 mm | 0.83" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 73 | 3,000 | 12 to 48 | 1.3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 4.1" | 1.7" | 3" | 6 mm | 18 mm | 0.83" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 142 | 3,000 | 12 to 70 | 3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 4.4" | 2.3" | 3.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.1" | Modbus TCP/IP, Ethernet/IP | 3 | 1 | 1 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 212 | 3,000 | 12 to 70 | 3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 5.3" | 2.3" | 3.2" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.1" | Modbus TCP/IP, Ethernet/IP | 3 | 1 | 1 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 212 | 3,000 | 12 to 70 | 3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 5.6" | 2.3" | 3" | 8 mm | 22.4 mm | 1.1" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 340 | 3,000 | 12 to 70 | 4 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 5.6" | 2.3" | 3.2" | 8 mm | 18 mm | 1.1" | Modbus TCP/IP, Ethernet/IP | 3 | 1 | 1 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 340 | 3,000 | 12 to 70 | 4.3 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 5.7" | 2.3" | 3" | 8 mm | 22.4 mm | 1.1" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 34 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 382 | 3,000 | 24 to 70 | 5.1 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 5.9" | 3.4" | 5" | 14 mm | 35 mm | 1.7" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 736 | 3,000 | 24 to 70 | 5.1 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 7" | 3.4" | 5" | 14 mm | 35 mm | 1.7" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 949 | 3,000 | 24 to 70 | 5.1 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 8.2" | 3.4" | 5" | 14 mm | 35 mm | 1.7" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,161 | 3,000 | 48 to 70 | 5.2 | 1 to 1/256 | 1.8° | 9.4" | 3.4" | 5" | 14 mm | 35 mm | 1.7" | Modbus RTU | 8 | 1 | 4 | IP20 | 0000000 | 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High-Temperature Stepper Motors
Motors
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia. | Lg. | Ctr.-to-Base Lg. | Type | No. of Shafts | Min. | Max. | Each | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 17 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 85.4 | 820 | 1.05 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 2.8" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 24 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | -40 | 212 | 0000000 | 0000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 115.1 | 975 | 2 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.285" | 1.7" | 1.7" | 5 mm | 24 mm | 0.84" | D-Profile | 1 | -40 | 212 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 181 | 1,000 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | -40 | 212 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 237 | 1,175 | 4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.9" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 1/4" | 3/4" | 1.13" | D-Profile | 1 | -40 | 212 | 0000000 | 000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clean Room Stepper Motors
Motors
Overall | Shaft | Temp. Range, ° F | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max. Holding Torque, in·ozf | Max. Rotation Speed, rpm | Max. Current per Phase, amp | Full Step Increment | Stepper Motor Polarity | No. of Wire Leads | Lg. | Wd. | Ht. | Dia., mm | Lg., mm | Type | No. of Shafts | Vacuum Rating, Torr | Min. | Max. | Clean Room Std. | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Square Body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NEMA 23 Frame Size | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 181 | 1,300 | 2.8 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 3.1" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 6 | 21 | D-Profile | 1 | 1× 10^-7 | 0 | 120 | ISO Class 1 | 0000000 | 000000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 237 | 2,000 | 4 | 1.8° | Bipolar | 4 | 4" | 2.3" | 2.3" | 6 | 21 | D-Profile | 1 | 1× 10^-7 | 0 | 120 | ISO Class 1 | 0000000 | 00000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||