How to Identify and Measure Fittings
Pipe size is an industry designation, not the actual size. View information about how to measure threaded and unthreaded pipe and pipe fittings.
More
Compression Fittings for Copper Tubing
- For Use With: Air, Cutting Oil, Fuel Oil, Hydraulic Fluid, Mineral Oil, Water
- Temperature Range: See Table
- Tubing: Use with copper
- Specifications Met: See Table
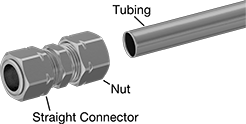
Create a strong connection without heating, flaring, or soldering. These fittings have a single sleeve (ferrule or olive) that bites into tubing as you tighten the nut. Both the nut and sleeve are included. Also known as single ferrule fittings, they are easier to install than yor-lok fittings which have two ferrules. They’re often used in low to medium pressure applications, such as plumbing and compressed air systems, which don’t require the strength of a yor-lok fitting. Compression fittings for copper tubing can withstand higher pressures than compression fittings for plastic and rubber tubing. Made of brass, they have good corrosion resistance.
To connect a compression fitting to tube, slide the nut and sleeve onto the tube. Then push the tube into the fitting until it butts against the back of the fitting. Tighten the nut onto the fitting to compress the sleeve.
Threaded connections can be taken apart as needed for maintenance and repair.
For technical drawings and 3-D models, click on a part number.
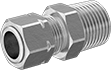
For Tube | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD | Wall Thick. | Thread Size | Thread Pitch, mm | Material | Max. Pressure | Temp. Range, °F | Each | |
Metric Threads | ||||||||
| 8mm | 1mm | M13 | 1.25 | Brass | 1,450 psi @ 72° F | -40° to 250° | 00000000 | 000000 |

For Tube | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD | Wall Thick. | Sleeve Material | Max. Pressure | Temp. Range, °F | Pkg. Qty. | Pkg. | |
| 8mm | Not Rated | Brass | 1,000 psi @ 72° F | -40° to 250° | 1 | 0000000 | 00000 |