How to Identify and Measure Fittings
Pipe size is an industry designation, not the actual size. View information about how to measure threaded and unthreaded pipe and pipe fittings.
More
About Gas Regulators
More
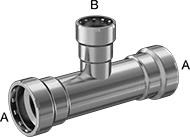
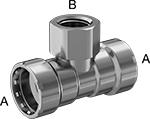
Low-Pressure Press-Connect Steel Unthreaded Pipe Fittings
- For Use On:
EPDM Rubber O-Ring: Ethylene Glycol, Propylene Glycol, Water
Buna-N Rubber O-Ring: Air, Lubricants, Propane, Fuel Oil, Natural Gas, Diesel Fuel - Specifications Met:
EPDM Rubber O-Ring: ASME B31,1, ASME B31.3, ASME B31.9, FM 1920, UL 213
Buna-N Rubber O-Ring: ASME B31.1, ASME B31.3, ASME B31.9, ANSI LC4/CSA 6.32, International Fuel Gas Code - Maximum Pressure:
EPDM Rubber O-Ring: 200 psi @ 72° F
Buna-N Rubber O-Ring: 125 psi @ 72° F - Pipe Nipples and Pipe: Use Schedule 40 Steel
- Flanges: Use Class 150 Steel
Crimp these fittings onto steel pipe to form a tightly sealed connection that’s faster than threading or welding and doesn’t require heat. An internal gripping ring and rubber O-ring create a secure seal when crimped. They are designed to leak if fittings have not been crimped; a colored dot marks the leak path so it's easy to spot unsealed connections. These steel fittings are coated in zinc-nickel to resist corrosion, but will rust if frequently exposed to saltwater or harsh chemicals. They are comparable to Viega MegaPress steel fittings.
Fittings meet ASME B31 code requirements for use in pressure piping systems.
Buna-N rubber O-rings hold up to natural gas, propane, diesel fuel, lubricants, and other oils. Fittings with these O-rings are often used in fuel gas systems and air lines. They meet the ANSI LC4/CSA 6.32 standard for fuel gas systems and comply with the International Fuel Gas Code.

Inline tees are also known as branch tees.
Buna-N Rubber O-Ring | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size | Socket Dp. | Each | |
NPT Threads | |||
| 3/4 | 0.188" | 00000000 | 000000 |

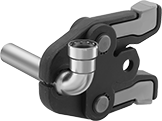
Crimping tools seal fittings in less than five seconds. These tools are cordless, so you can take them to any job. Connect the jaw or ring that matches your pipe size to these tools, then pull the trigger to crimp the fitting. The pivoting head lets you access connections from any angle.
Battery | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | No. Included | Cap., amp-hrs. | Battery Charger Included | Battery Charging Time, min. | Compatible With | Each | |
| 18V DC | 2 | 3 | Yes | 39 | Viega MegaPress Viega ProPress Viega ProPress XL-C | 00000000 | 000000000 |

Jaw and ring sets include three jaws, three rings, and one ring actuator jaw. Jaws are for pipe sizes 1/2 to 1; they fit directly into the crimping tool. Rings are for pipe sizes 1 1/4 to 2; clip the ring around the fitting and use the ring actuator jaw and crimping tool to press the open ends together.
For Pipe | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Material | For Manufacturer | For Manufacturer Model No. | Compatible With | Includes | Container Type | Each | |
| 1/2, 3/4, 1, 1 1/4, 1 1/2, 2 | Stainless Steel, Steel | Ridgid | RP 340 | Viega MegaPress | One Ring Actuator Jaw Three Jaws (1/2-1 Pipe Size) Three Rings (1 1/4-2 Pipe Size) | Carrying Case | 00000000 | 000000000 |
Tank-Mount Pressure-Regulating Valves for Fuel Gases
- For Use With: See Table
- Temperature Range: -20° to 120° F
Attach these valves to acetylene, hydrogen, methane, propane, or propylene tanks to reduce a high inlet pressure to a lower, stable outlet pressure. They have Compressed Gas Association (CGA) numbered inlet fittings for secure connections to compressed gas tanks. Choose a valve with the same CGA number as your tank and other system components. Valves come with a gauge to monitor outlet pressure and a gauge to monitor inlet pressure from the tank.
Choose a valve with a maximum outlet pressure that’s approximately twice your application’s normal operating pressure. Your operating pressure should never exceed 75% of the valve’s maximum outlet pressure.
Single-stage valves reduce pressure in one step, which causes the outlet pressure to fluctuate slightly as you empty the tank. They’re best for applications where a constant outlet pressure isn’t critical.
Two-stage valves progressively reduce pressure over two steps for more consistent outlet pressure at all times. They’re often used in applications that require a constant outlet pressure regardless of the tank level.
Valves with a brass body have a longer service life than valves with a brass and steel body.


Inlet | Outlet | Material | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA Number | Location | Thread Direction | Pressure Gauge Range, psi | Thread Size | Location | Thread Direction | Pressure Range, psi | Pressure Adjustment Method | Body | Seal | Diaphragm | Each | |
For Use With Propane and Propylene | |||||||||||||
UNF Male Outlet × NGO Male Inlet | |||||||||||||
| CGA 510 | Side | Left Hand | 0 to 400 | 9/16"-18 | Side | Left Hand | 0 to 50 | T-Handle | Brass | PTFE | Rubber | 0000000 | 0000000 |
| CGA 510 | Side | Left Hand | 0 to 400 | 9/16"-18 | Side | Left Hand | 5 to 50 | Knob | Brass/Steel | PTFE | Rubber | 0000000 | 000000 |

Inlet | Outlet | Material | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA Number | Location | Thread Direction | Pressure Gauge Range, psi | Thread Size | Location | Thread Direction | Pressure Range, psi | Pressure Adjustment Method | Body | Seal | Diaphragm | Each | |
For Use With Propane and Propylene | |||||||||||||
UNF Male Outlet × NGO Male Inlet | |||||||||||||
| CGA 510 | Side | Left Hand | 0 to 400 | 9/16"-18 | Side | Left Hand | 0 to 50 | T-Handle | Brass/Steel | PTFE | Rubber | 0000000 | 0000000 |
Pressure-Regulating Valves for Fuel Gases

- For Use With: See table
- Temperature Range: See table
Install these valves directly in gas distribution pipelines for acetylene, hydrogen, or propane. They automatically reduce a high inlet pressure to a lower, stable outlet pressure. Valves have two outlets to fit various pipe configurations and come with a plug to close the unused outlet. The gauge monitors outlet pressure. All valves are single stage and reduce pressure in one step, which causes the outlet pressure to fluctuate.
Choose a valve with a maximum outlet pressure that’s approximately twice your application’s normal operating pressure. Your operating pressure should never exceed 75% of the valve’s maximum outlet pressure.
Inlet | Outlet | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For Use With | Pipe Size | Location | Max. Pressure, psi | Pipe Size | Location | Pressure Adjustment Method | Pressure Gauge Range, psi | Temperature Range, °F | End-to-End Lg. | Port-to-Port Lg. | Each | |
NPT Female | ||||||||||||
Brass Body—Stainless Steel Diaphragm and Neoprene Seal | ||||||||||||
| Hydrogen, Propane | 1/4 | Side | 500 | 1/4 | Bottom, Side | T-Handle | 0 to 60 | 0° to 120° | 2.40" | 1.01" | 0000000 | 0000000 |
| Hydrogen, Propane | 1/4 | Side | 500 | 1/4 | Bottom, Side | T-Handle | 0 to 200 | 0° to 120° | 2.40" | 1.01" | 0000000 | 000000 |