Filter by
Thread Size
System of Measurement
Thread Direction
Flute Type
Sold As
Finish
Material
Number of Flutes
Shank Type
DFARS Specialty Metals
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
For Threading
REACH
RoHS
Drill Bit Decimal Size Equivalent
Number of Tapping Ends
For Hole Type
Performance
Taps
Cut threads into holes so screws, bolts, and rods fit snugly. Our basic taps have straight flutes that are good for most jobs.
High-Speed Steel—The most versatile taps resist heat and wear to stay sharp. They’re good for most metals and plastic.
Uncoated—The economical choice, these won't last as long as coated taps.
Plug Chamfer—Our go-to chamfer type, these thread both through holes and blind holes. The tapered section is shorter than a taper chamfer and longer than bottoming chamfer. As a result, they're easier to turn than bottoming taps but require more force than taper taps.
Bottoming Chamfer—Cut all the way to the bottom of blind holes with taps that have the shortest taper. Since these require the most force to turn, they’re often used to finish holes started by taper- or plug-chamfer taps.
Number of Flutes—Taps with fewer flutes have more space to capture chips, so you won’t have to clear them as often. However, they can be more difficult to keep straight in the hole.
Chip-Clearing Taps
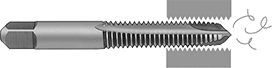 |
Spiral-Point Flute for Through Holes |
Remove long, stringy chips to produce cleaner threads than standard taps. The flute design prevents buildup to protect the quality of the threads and avoid damage to the tap. Since you don’t need to reverse these taps to extract chips, they also create threads faster.
High-Speed Steel—The most versatile taps resist heat and wear to stay sharp. They’re good for most metals and plastic.
Black Oxide—The dark finish increases wear resistance and reduces friction to improve chip flow, so these taps can last 50% longer than uncoated taps.
Spiral-Point Flute for Through Holes—Push chips ahead of the tap and out of through holes. Also known as gun taps.
Plug Chamfer—Our go-to chamfer type. With a longer taper than a bottoming chamfer, they are easier to turn but won't thread as close the bottom of a hole.
Drill Bit | Spiral-Point Flute for Through Holes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Thread Size | Thread Lg. | Overall Lg. | Thread Type | Size | Decimal Size Equiv. | Shank Type | Chamfer Type | No. of Flutes | Each | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High-Speed Steel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Black Oxide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 1/4"-8 | 1.71" | 5 3/4" | UNF | 1 1/8" | 1.125" | Square | Plug | 4 | 2523A83 | 0000000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||